Virtualization is being used by a growing number of organizations and the concept of virtualization can simplify the operations in the IT sector and allows these organizations to respond faster to changing demands.
What you mean by Virtualization ???
Virtualization is the process of creating a virtual environment on an
existing server to run your desired program, without interfering with
any of the other services provided by the server or host platform to
other users.
In computing, Virtualization refers to the process of creating a “virtual” version of something – such as an operating system (OS), a server, network resources or a storage device.
So, What does the Virtualization Do ??
It allows you to run multiple applications and operating systems on the same server, (making use of one server & this server is being shared among multiple machines) which provides efficient resource utilization and helps in reducing costs.

In other words, Virtualization is a technique, which allows to share a single physical instance of a resource or an application among multiple customers and organizations. It does by assigning a logical name to a physical storage and providing a pointer to that physical resource when demanded.
Virtualization plays a very important role in the
cloud computing technology, normally in the cloud computing, users share
the data present in the clouds like application etc, but actually with
the help of virtualization users shares the Infrastructure.
The Virtual environment can be a single instance or a
combination of many such as operating systems, Network or Application
servers, computing environments, storage devices, and other such
environments
The machine on which the virtual machine is going to create is known as Host Machine and that virtual machine is referred as a Guest Machine.
This virtual machine is managed by a software or firmware, which is known as hypervisor.
Hypervisor acts as a link between the hardware and the virtual environment and distributes the hardware resources such as CPU usage, memory allotment between the different virtual environments.
Working Of Virtualization
With virtualization, an application, a guest OS or data storage is separated from the underlying software or hardware. A thin software layer, known as a hypervisor, which partitions, or more specifically, abstracting and isolating these different OS and applications from the underlying computer hardware. Therefore, it wouldn’t be incorrect to say that virtualization is enabled by the functions of the hypervisor.
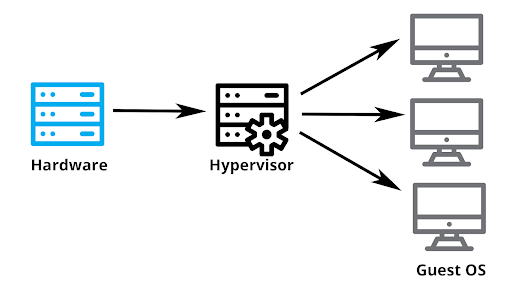
After virtualization, different user applications managed by their own operating systems (guest OS) can run on the same hardware, independent of the host OS. This is often done by adding additional software, called a virtualization layer. This virtualization layer is known as hypervisor or virtual machine monitor (VMM). The VMs are shown in the upper boxes, where applications run with their own guest OS over the virtualized CPU, memory, and I/O resources.
What this means is that the underlying hardware (which is known as the host machine) can independently operate and run one or more virtual machines (known as guest machines). The hypervisor also helps manage these independent Virtual Machines by distributing hardware resources such as memory allotment, CPU usage network bandwidth and more amongst them. It does this by creating pools of abstracted hardware resources, which it then allocates to Virtual Machines. It also can stop and start virtual machines, when requested by the user.
Another key component of hypervisors is ensuring that all the Virtual Machines stay isolated from others – so when a problem occurs in one Virtual Machine, the others remain unaffected. Finally, the hypervisor also handles the communication amongst Virtual Machines over virtual networks – enabling VMs to connect with one another.
The most common form is known as Type 1, where the layer sits on the hardware and virtualizes the hardware platform so that multiple virtual machines can utilize it. A type 2 hypervisor, on the other hand, uses a host operating system to create isolated guest virtual machines.
Each virtual server mimics the functionalities of a dedicated server –
on one server. Each server is then designated an individual and separate
OS, software and rebooting provisions, via root access. In a virtual
server environment, website admins and ISPs can have separate and
different domain names, IP addresses, analytics, logs, file directories
email administration and more. Security systems and passwords also
function separately, as it would in a dedicated server environment.
Numerous benefits are provided by virtualization which includes, reduction in costs, efficient utilization of resources, better accessibility, and minimization of risk among others.
Features
- Partitioning: Multiple virtual servers can run on a physical server at the same time.
- Encapsulation of data: All data on the virtual server, including boot disks, is encapsulated in a file format.
- Isolation: The Virtual server running on the physical server is safely separated and don't affect each other.
- Hardware Independence: When the virtual server runs, it can migrate to a different hardware platform.
Advantages
- The number of servers gets reduced by the use of the virtualization concept.
- Improve the ability of technology.
- The business continuity was also raised due to the use of virtualization.
- It creates a mixed virtual environment.
- Increase efficiency for the development and test environment.
- Lowers Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
Cloud V/S Virtualization
- Essentially there is a gap between these two terms, though cloud technology requires the concept of virtualization. Virtualization is a technology - it can also be treated as software that can manipulate hardware. At the same time, cloud computing is a service that is the result of manipulation.
- Virtualization is the foundation element of cloud computing, whereas Cloud technology is the delivery of shared resources as a service-on-demand via the internet.
- Cloud is essentially made-up of the concept of virtualization.
Types of Virtualization
- Hardware Virtualization
- Software Virtualization
- OS Virtualization
- Server Virtualization
- Storage Virtualization
#Hardware Virtualization
Virtualization means abstraction. Hardware virtualization is accomplished by abstracting the physical hardware layer by use of a hypervisor or VMM (Virtual Machine Monitor).
When the virtual machine software or virtual machine manager (VMM) or hypervisor software is directly installed on the hardware system is known as hardware virtualization.
The primary task of the hypervisor is to process monitoring, memory & hardware controlling. After hardware virtualization is done, different operating systems can be installed, and various applications can run on it.
Hardware virtualization, when done for server platforms, is also called server virtualization. Hardware virtualization is mainly done for the server platforms, because controlling virtual machines is much easier than controlling a physical server.
Hardware virtualization is of three kinds.
- Full Virtualization: Here, the hardware architecture is completely simulated. Guest software doesn't need any modification to run any applications.
- Emulation Virtualization: Here, the virtual machine simulates the hardware & is independent. Furthermore, the guest OS doesn't require any modification.
- Para-Virtualization: Here, the hardware is not simulated; instead, the guest software runs its isolated system.
Advantages
- Lower Cost: Because of server consolidation, the cost decreases; now, multiple OS can exist together in a single hardware. This minimizes the quantity of rack space, reduces the number of servers, and eventually drops the power consumption.
- Efficient resource utilization: Physical resources can be shared among virtual machines. Another virtual machine can use the unused resources allocated by one virtual machine in case of any need.
- Increase IT flexibility: The quick development of hardware resources became possible using virtualization, and the resources can be managed consistently also.
- Advanced Hardware Virtualization features: With the advancement of modern hypervisors, highly complex operations maximize the abstraction of hardware & ensure maximum uptime. This technique helps to migrate an ongoing virtual machine from one host to another host dynamically.
#Software Virtualization
It is also called application virtualization is the practice of running software from a remote server.
Software virtualization is similar to that of virtualization except that it is capable to abstract the software installation procedure and create virtual software installation.
Many applications & their distributions became typical tasks for IT firms and departments. The mechanism for installing an application differs. So virtualized software is introduced which is an application that will be installed into its self-contained unit and provide software virtualization.
Some of the examples are Virtual Box, VMware, etc.
The DLL (Data Link Layer) redirect the entire virtualized program's
calls to the file system of the server. When the software is run from
the server in this procedure, no changes are required to be made on the
local system.
Types
- Operating System Virtualization – hosting multiple OS on the native OS
- Application Virtualization – hosting individual applications in a virtual environment separate from the native OS
- Service Virtualization – hosting specific processes and services related to a particular application
Advantages
- Ease of Client Deployment: Virtual software makes it easy to link a file in a network or file copying to the workstation.
- Software Migration: Before the concept of virtualization, shifting from one software platform to another was time-consuming; and has a significant impact on the end-system user. The software virtualization environment makes migration easier.
- Easy to Manage: Application updates become a simple task.
#Server Virtualization
It is the division of physical server into several virtual servers and this division is mainly done to improvise the utility of server resource.
In other word it is the masking of resources that are located in server which includes the number & identity of processors, physical servers & the operating system. This division of one physical server into multiple isolated virtual servers is done by server administrator using software.
The virtual environment is sometimes called the virtual private-servers.
In this process, the server resources are kept hidden from the user. This partitioning of physical server into several virtual environments; result in the dedication of one server to perform a single application or task.
For Server Virtualization, there are three popular approaches.
- Virtual Machine model
- Para-virtual Machine model
- Operating System (OS) layer Virtualization
Server virtualization can be viewed as a part of overall virtualization trend in the IT companies that include network virtualization, storage virtualization & management of workload. This trend brings development in automatic computing. Server virtualization can also used to eliminate server sprawl (Server sprawl is a situation in which many under-utilized servers utilize more space or consume more resources than can be justified by their workload) & uses server resources efficiently.
- Virtual Machine model: are based on host-guest paradigm, where each guest runs on a virtual replica of hardware layer. This technique of virtualization provide guest OS to run without modification. However it requires real computing resources from the host and for this a hypervisor or VM is required to coordinate instructions to CPU.
- Para-Virtual Machine model: is also based on host-guest paradigm & uses virtual machine monitor too. In this model the VMM modifies the guest operating system's code which is called 'porting'. Like that of virtual machine, similarly the Para-virtual machine is also capable of executing multiple operating systems. The Para-virtual model is used by both Xen & UML.
- Operating System Layer Virtualization: Virtualization at OS level functions in a different way and is not based on host-guest paradigm. In this model the host runs a single operating system kernel as its main/core and transfers its functionality to each of the guests. The guest must use the same operating system as the host. This distributed nature of architecture eliminated system calls between layers and hence reduces overhead of CPU usage. It is also a must that each partition remains strictly isolated from its neighbors because any failure or security breach of one partition won't be able to affect the other partitions. OS-Level Virtualization never uses a hypervisor.
- Cost Reduction: Server virtualization reduces cost because less hardware is required.
- Independent Restart: Each server can be rebooted independently and that reboot won't affect the working of other virtual servers.
- Disaster Recovery: Disaster Recovery is one of the best advantages of Server Virtualization. In Server Virtualization, data can easily and quickly move from one server to another and these data can be stored and retrieved from anywhere.
- Faster deployment of resources: Server virtualization allows us to deploy our resources in a simpler and faster way.
- Security: It allows uses to store their sensitive data inside the data centers.
Disadvantages of Server Virtualization
There are the following disadvantages of Server Virtualization -
- The biggest disadvantage of server virtualization is that when the server goes offline, all the websites that are hosted by the server will also go down.
- There is no way to measure the performance of virtualized environments.
- It requires a huge amount of RAM consumption.
- It is difficult to set up and maintain.
- Some core applications and databases are not supported virtualization.
- It requires extra hardware resources.
Uses of Server Virtualization
A list of uses of server virtualization is given below -
- Server Virtualization is used in the testing and development environment.
- It improves the availability of servers.
- It allows organizations to make efficient use of resources.
- It reduces redundancy without purchasing additional hardware components.
#Storage Virtualization
It pools the physical storage from different network storage devices and makes it appear to be a single storage unit that is handled from a single console. As we all know there has been a strong bond between physical host & locally installed storage device; and with the change in paradigm, local storage is no longer needed. More advanced storage has come to the market with an increase in functionality. Storage virtualization is the significant component of storage servers & facilitates management and monitoring of storage in a virtualized environment.
Storage virtualization helps the storage administrator to backup, archive and recovery data more efficiently, in less amount of time by masking the actual complexity of SAN (Storage Area Network). Through the use of software hybrid appliances, the storage administrator can implement virtualization.
Storage virtualization is becoming more and more important in different forms such as:
- Storage Tiering: Using the storage technique as a bridge or as a stepping stone, this technique analyzes and select out the most commonly used data & place it on its highest performing storage pool and the least used data in the weakest performance storage pool.
- WAN Environment: Instead of sending multiple copies of the same data over WAN, WAN accelerator is used to locally cache the data and present it in a LAN speed, and not impacting the WAN performance.
- SAN Storage: SAN technology present the storage as block-level storage & the storage is presented over the Ethernet network of OS.
- File Server: OS writes the data to a remote server location to keep it separate and secure from local users.
- Data is stored in a very convenient location. This is because if the host failure data don't get compromised necessarily.
- By using storage level abstraction, it becomes flexible how storage is provided, protected, partitioned and used.
- Storage Devices are capable of performing advanced functions such as disaster recovery, duplication, replication of data & re-duplication of data
Desktop virtualization is technology that lets users simulate a workstation load to access a desktop from a connected device remotely or locally. This separates the desktop environment and its applications from the physical client device used to access it. Desktop virtualization is a key element of digital workspace and depends on application virtualization.
How does desktop virtualization work?
Desktop virtualization can be achieved in a variety of ways, but the most important two types of desktop virtualization are based on whether the operating system instance is local or remote.
Local Desktop Virtualization
Local desktop virtualization means the operating system runs on a client device using hardware virtualization, and all processing and workloads occur on local hardware. This type of desktop virtualization works well when users do not need a continuous network connection and can meet application computing requirements with local system resources. However, because this requires processing to be done locally you cannot use local desktop virtualization to share VMs or resources across a network to thin clients or mobile devices.
Remote Desktop Virtualization
Remote desktop virtualization is a common use of virtualization that operates in a client/server computing environment. This allows users to run operating systems and applications from a server inside a data center while all user interactions take place on a client device. This client device could be a laptop, thin client device, or a smartphone. The result is IT departments have more centralized control over applications and desktops, and can maximize the organization’s investment in IT hardware through remote access to shared computing resources.
What is virtual desktop infrastructure?
A popular type of desktop virtualization is virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI). VDI is a variant of the client-server model of desktop virtualization which uses host-based VMs to deliver persistent and nonpersistent virtual desktops to all kinds of connected devices. With a persistent virtual desktop, each user has a unique desktop image that they can customize with apps and data, knowing it will be saved for future use. A nonpersistent virtual desktop infrastructure allows users to access a virtual desktop from an identical pool when they need it; once the user logs out of a nonpersistent VDI, it reverts to its unaltered state. Some of the advantages of virtual desktop infrastructure are improved security and centralized desktop management across an organization.
What are the benefits of desktop virtualization?
- Resource Management:
Desktop virtualization helps IT departments get the most out of their hardware investments by consolidating most of their computing in a data center. Desktop virtualization then allows organizations to issue lower-cost computers and devices to end users because most of the intensive computing work takes place in the data center. By minimizing how much computing is needed at the endpoint devices for end users, IT departments can save money by buying less costly machines. - Remote work:
Desktop virtualization helps IT admins support remote workers by giving IT central control over how desktops are virtually deployed across an organization’s devices. Rather than manually setting up a new desktop for each user, desktop virtualization allows IT to simply deploy a ready-to-go virtual desktop to that user’s device. Now the user can interact with the operating system and applications on that desktop from any location and the employee experience will be the same as if they were working locally. Once the user is finished using this virtual desktop, they can log off and return that desktop image to the shared pool. - Security:
Desktop virtualization software provides IT admins centralized security control over which users can access which data and which applications. If a user’s permissions change because they leave the company, desktop virtualization makes it easy for IT to quickly remove that user’s access to their persistent virtual desktop and all its data—instead of having to manually uninstall everything from that user’s devices. And because all company data lives inside the data center rather than on each machine, a lost or stolen device does not post the same data risk. If someone steals a laptop using desktop virtualization, there is no company data on the actual machine and hence less risk of a breach.
What is Server Virtualization?
Server virtualization is used to mask server resources from server users. This can include the number and identity of operating systems, processors, and individual physical servers.
Server Virtualization Definition
Server virtualization is the process of dividing a physical server into multiple unique and isolated virtual servers by means of a software application. Each virtual server can run its own operating systems independently.
Key Benefits of Server Virtualization:
- Higher server ability
- Cheaper operating costs
- Eliminate server complexity
- Increased application performance
- Deploy workload quicker
Three Kinds of Server Virtualization:
- Full Virtualization: Full virtualization uses a hypervisor, a type of software that directly communicates with a physical server's disk space and CPU. The hypervisor monitors the physical server's resources and keeps each virtual server independent and unaware of the other virtual servers. It also relays resources from the physical server to the correct virtual server as it runs applications. The biggest limitation of using full virtualization is that a hypervisor has its own processing needs. This can slow down applications and impact server performance.
- Para-Virtualization: Unlike full virtualization, para-virtualization involves the entire network working together as a cohesive unit. Since each operating system on the virtual servers is aware of one another in para-virtualization, the hypervisor does not need to use as much processing power to manage the operating systems.
- OS-Level Virtualization: Unlike full and para-virtualization, OS-level visualization does not use a hypervisor. Instead, the virtualization capability, which is part of the physical server operating system, performs all the tasks of a hypervisor. However, all the virtual servers must run that same operating system in this server virtualization method.
Why Server Virtualization?
Server virtualization is a cost-effective way to provide web hosting services and effectively utilize existing resources in IT infrastructure. Without server virtualization, servers only use a small part of their processing power. This results in servers sitting idle because the workload is distributed to only a portion of the network’s servers. Data centers become overcrowded with underutilized servers, causing a waste of resources and power.
By having each physical server divided into multiple virtual servers, server virtualization allows each virtual server to act as a unique physical device. Each virtual server can run its own applications and operating system. This process increases the utilization of resources by making each virtual server act as a physical server and increases the capacity of each physical machine.
https://www.w3schools.in/cloud-virtualization/os-virtualization/
https://www.w3schools.in/cloud-computing/cloud-virtualization/#Types_of_Virtualization
https://www.javatpoint.com/cloud-computing-data-virtualization
https://www.redswitches.com/blog/virtualization-types-cloud-computing/
https://www.atlantic.net/vps-hosting/what-is-server-virtualization/https://www.brainkart.com/article/Virtualization-Structures-Tools-and-Mechanisms_11333/