- The term cloud refers to a network or the internet.
- CC is a technology that uses remote servers on the internet to store, manage, and access data online rather than local drives.
- The data can be anything such as files, images, documents, audio, video, and more.
- Cloud computing provides shared services as opposed to local servers or storage resources, enables access to information from most web-enabled hardware and allows for cost savings – reduced facility, hardware/software investments, support.
There are the following operations that we can do using cloud computing:
- Developing new applications and services
- Storage, back up, and recovery of data
- Hosting blogs and websites
- Delivery of software on demand
- Analysis of data
- Streaming videos and audios
Why Cloud Computing?
Small as well as large IT companies, follow the traditional methods to provide the IT infrastructure. That means for any IT company, we need a Server Room that is the basic need of IT companies.
In that server room, there should be a database server, mail server, networking, firewalls, routers, modem, switches, QPS (Query Per Second means how much queries or load will be handled by the server), configurable system, high net speed, and the maintenance engineers.
To establish such IT infrastructure, we need to spend lots of money. To overcome all these problems and to reduce the IT infrastructure cost, Cloud Computing comes into existence.
- File storage: You can store all types of information in the cloud, including files and email. ...
- File sharing: The cloud makes it easy to share files with several people at the same time. ...
- Backing up data: You can also use the cloud to protect your files.
Characteristics of Cloud Computing
1. On-demand self-service- A consumer can unilaterally ("one-sided") provide or offer computing capabilities, such as server time and network storage, as needed automatically without requiring human interaction with each service provider.
2. Broad network access- Capabilities are available over the network and accessed through standard mechanisms that promote use by heterogeneous thin or thick client platforms (e.g., mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and workstations).
3. Resource pooling- The provider’s computing resources are pooled (grouping together of resources for the purposes of maximizing advantage or minimizing risk to the users) to serve multiple consumers. Resources can be dynamically assigned and reassigned according to customer demand. Customer generally may not care where the resources are physically located but should be aware of risks if they are located offshore
4. Rapid elasticity- Capabilities can be expanded or released automatically (i.e., more CPU power, or ability to handle additional users). To the customer this appears seamless, limitless, and responsive to their changing requirements.
5. Measured service- Customers are charged for the services they use. There is a metering concept where customer resource usage can be monitored, controlled, and reported, providing transparency for both the provider and consumer of the utilized service.
1) Agility
The cloud works in a distributed computing environment. It shares resources among users and works very fast.
2) High availability and reliability
The availability of servers is high and more reliable because the chances of infrastructure failure are minimum.
3) High Scalability
Cloud offers "on-demand" provisioning of resources on a large scale, without having engineers for peak loads.
4) Multi-Sharing
With the help of cloud computing, multiple users and applications can work more efficiently with cost reductions by sharing common infrastructure.
5) Device and Location Independence
Cloud computing enables the users to access systems using a web browser regardless of their location or what device they use e.g. PC, mobile phone, etc. As infrastructure is off-site (typically provided by a third-party) and accessed via the Internet, users can connect from anywhere.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
1) Back-up and restore data
Once the data is stored in the cloud, it is easier to get back-up and restore that data using the cloud.
2) Improved collaboration
Cloud applications improve collaboration by allowing groups of people to quickly and easily share information in the cloud via shared storage.
3) Excellent accessibility
Cloud allows us to quickly and easily access store information anywhere, anytime in the whole world, using an internet connection. An internet cloud infrastructure increases organization productivity and efficiency by ensuring that our data is always accessible.
4) Low maintenance cost
Cloud computing reduces both hardware and software maintenance costs for organizations. Maintenance of cloud computing applications is easier, since they do not need to be installed on each user's computer and can be accessed from different places. So, it reduces the cost also.
5) Mobility
Cloud computing allows us to easily access all cloud data via mobile.
6) Services in the pay-per-use model
Cloud computing offers Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to the users for access services on the cloud and pays the charges as per the usage of service.
7) Unlimited storage capacity
Cloud offers us a huge amount of storing capacity for storing our important data such as documents, images, audio, video, etc. in one place.
8) Data security
Data security is one of the biggest advantages of cloud computing. Cloud offers many advanced features related to security and ensures that data is securely stored and handled.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
1) Internet Connectivity
As you know, in cloud computing, every data (image, audio, video, etc.) is stored on the cloud, and we access these data through the cloud by using the internet connection. If you do not have good internet connectivity, you cannot access these data. However, we have no any other way to access data from the cloud.
2) Vendor lock-in
Vendor lock-in is the biggest disadvantage of cloud computing. Organizations may face problems when transferring their services from one vendor to another. As different vendors provide different platforms, that can cause difficulty moving from one cloud to another.
3) Limited Control
As we know, cloud infrastructure is completely owned, managed, and monitored by the service provider, so the cloud users have less control over the function and execution of services within a cloud infrastructure.
4) Security
Although cloud service providers implement the best security standards to store important information. But, before adopting cloud technology, you should be aware that you will be sending all your organization's sensitive information to a third party, i.e., a cloud computing service provider. While sending the data on the cloud, there may be a chance that your organization's information is hacked by Hackers.
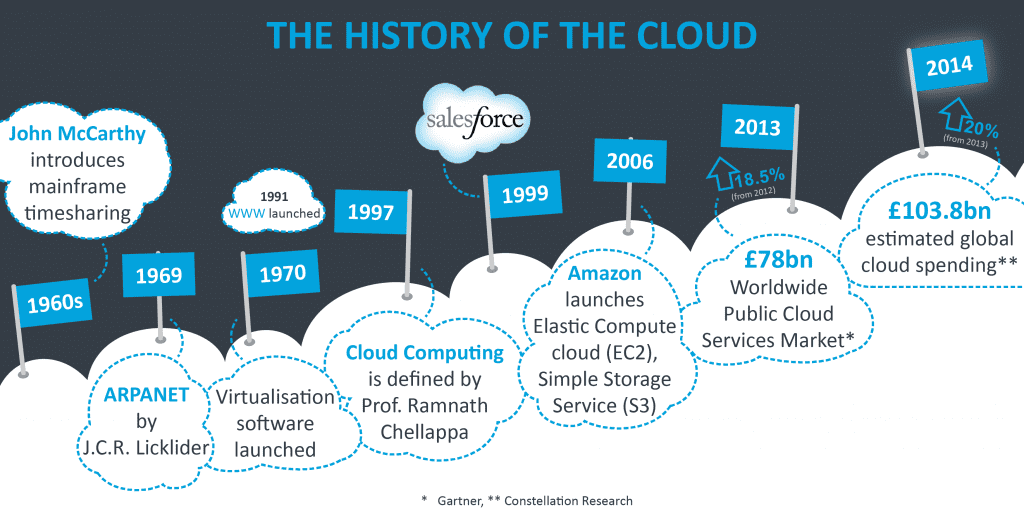
Evolution of CC
Cloud computing has its roots as far back in 1950s when mainframe computers came into existence.
In making cloud computing what it is today, five technologies played a vital role. These are distributed systems and its peripherals, virtualization, web 2.0, service orientation, and utility computing.
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/evolution-of-cloud-computing/
https://www.javatpoint.com/history-of-cloud-computing
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cloud_computing