Unlike traditional SQL databases, NoSQL databases, or “non-SQL” databases, do not store their data in tabular relations. Originally designed for modern web-scale databases, they have found widespread use in present-day big data and real-time web applications. Some of the most commonly used data structures include key-value, wide column, graph, and document stores.
As NoSQL databases do not adhere to a strict schema, they can handle large volumes of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. This allows developers to be more agile and push code changes much more quickly than with relational databases. In this article, we compare three popular open-source NoSQL databases and discuss how their specific use cases and features might be a good fit for your application.
CASE STUDY
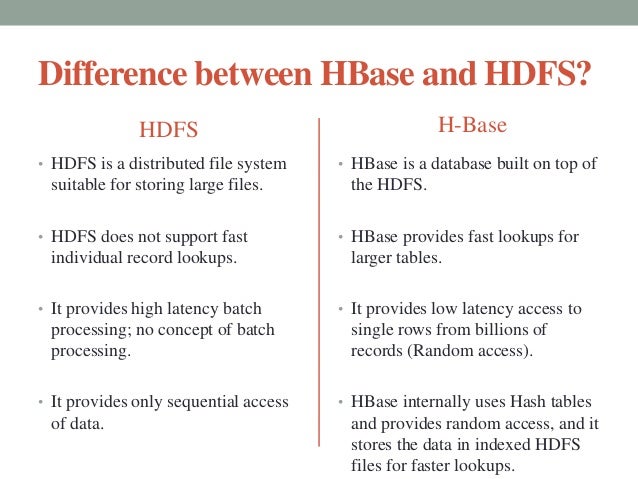
1. HDFS
- The Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) is the primary data storage system used by Hadoop applications.
- Hadoop itself is an open source distributed processing framework that
manages data processing and storage for big data applications. HDFS is a
key part of the many Hadoop ecosystem technologies, which provides a
reliable means for managing pools of big data and supporting related big data analytics applications.
- HDFS holds very large amount of data and provides easier access.
- To store such huge data, the files are stored across multiple machines. These files are stored in redundant fashion to rescue the system from possible data losses in case of failure.
- HDFS also makes applications available to parallel processing.
- It is used to scale a single Apache Hadoop cluster to hundreds (and even thousands) of nodes. .
- Unlike other distributed systems, HDFS is highly fault tolerant and designed using low-cost hardware.
- Coming to the architecture, HDFS employs a NameNode and DataNode to implement a distributed file system that provides high-performance access to data across highly scalable Hadoop clusters.
- Here, the data is split into multiple blocks and these blocks are then randomly distributed and stored across slave machines.
- Replicated three times & each block contains 128 MB of data by default & block size can also be customized.
- NameNode (Masternode): Contains metadata in RAM and disk
- Secondary NameNode: Contains a copy of NameNode’s metadata on disk
- Slave/Data Node: Contains the actual data in the form of blocks
Features of HDFS
- It is suitable for the distributed storage and processing.
- Hadoop provides a command interface to interact with HDFS.
- The built-in servers of namenode and datanode help users to easily check the status of cluster.
- Streaming access to file system data.
- HDFS provides file permissions and authentication.
2. HBase
- HBase is a open source, non-relational database management system that runs on top of Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS).
- It was modeled after Google's Bigtable and written in Java.
- It is developed as part of Apache Software Foundation's Apache Hadoop project and runs on top of HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System) or Alluxio, providing Bigtable-like capabilities for Hadoop. That is, it provides a fault-tolerant way of storing large quantities of sparse data.
- HBase is a wide-column store and has been widely adopted because of its lineage with Hadoop and HDFS.
- HBase is well-suited for faster read and write operations on large datasets with high throughput and low input/output latency.
- An HBase system is designed to scale linearly. It comprises a set of standard tables with rows and columns, much like a traditional database. Each table must have an element defined as a primary key, and all access attempts to HBase tables must use this primary key.
- Unlike relational database systems, HBase does not support a structured query language like SQL; in fact, HBase isn’t a relational data store at all.
HBase does support writing applications in Apache Avro, REST and Thrift.
Avro, as a component, supports a rich set of primitive data types including: numeric, binary data and strings; and a number of complex types including arrays, maps, enumerations and records. A sort order can also be defined for the data.
HBase relies on ZooKeeper for high-performance coordination. ZooKeeper is built into HBase, but if you’re running a production cluster, it’s suggested that you have a dedicated ZooKeeper cluster that’s integrated with your HBase cluster.
HBase works well with Hive, a query engine for batch processing of big data, to enable fault-tolerant big data applications.
Features
- Linear and modular scalability: As data sets are distributed over HDFS, thus it is linearly
scalable across various nodes, as well as modularly scalable, as it is
divided across various nodes.
- Strictly consistent reads and writes: HBase provides consistent reads and writes due to above feature.
- Automatic and configurable sharding of tables: HBase tables are distributed across clusters and these clusters are distributed across regions. These regions and clusters split, and are redistributed as the data grows.
- Automatic failover support between RegionServers: HBase with HDFS provides WAL (Write Ahead Log) across clusters which provides automatic failure support.
- Convenient base classes for backing Hadoop MapReduce jobs with Apache HBase tables.
- Easy to use Java API for client access: It provides easy to use Java API for programmatic access.
- Block cache and Bloom Filters for real-time queries: HBase supports a Block Cache and Bloom Filters for high volume query optimization .
- Query predicate push down via server side Filters
- Thrift gateway and a REST-ful Web service that supports XML, Protobuf, and binary data encoding options: It also supports Thrift and REST API for non-Java front-ends.
- Extensible jruby-based (JIRB) shell
- Support for exporting metrics via the Hadoop metrics subsystem to files or Ganglia; or via JMX.
HBase Advantages and Use Cases
One of the strengths of HBase is its use of HDFS as the distributed file system. This allows the database to store large data sets, even billions of rows, and provide analysis in a short period. This support for sparse data, along with the fact that it can be hosted/distributed across commodity server hardware, ensures that the solution is very cost-effective when the data is scaled to gigabytes or petabytes. That distribution contributes to one of its big pros: fail over support includes automatic recovery.
Several concepts from Bigtable, like Bloom filters and block caches, can also be used for query optimization. HBase also has a leg up in any HBase vs. Cassandra comparison when it comes to consistency, as the reads and writes adhere to immediate consistency, compared to the eventual consistency in Cassandra. Its close integration with Hadoop projects and MapReduce makes it an enticing solution for Hadoop distributions.
#Some of HBase’s common use cases include online log analytics, Hadoop distributions, write-heavy applications, and applications in need of large volume (like Tweets, Facebook posts, etc.).
HBase Disadvantages
Although HBase shares several similarities with Cassandra, one major difference in its architecture is the use of a master-slave architecture. This also proves to be a single point of failure, as failing from one HMaster to another can take time, which can also be a performance bottleneck. If you are looking for an always-available system, then Cassandra might be a better choice.
Unlike Cassandra, HBase does not have a query language. This means that to achieve SQL-like capabilities, one must use the JRuby-based HBase shell and technologies like Apache Hive (which, in turn, is based on MapReduce). The major problem with this approach is the high latency and steep learning curve in employing these technologies.
Although HBase scales well by adding DataNodes to its cluster, it has some high hardware requirements, mainly because of its dependency on HDFS, which would require five DataNodes and one NameNode as a minimum. This, in turn, translates to high running and maintenance costs.
Another important factor to consider when choosing HBase is its interdependency on other systems, like HDFS, for storage, and Apache ZooKeeper for status management and metadata. So, when designing solutions, the architecture might become complex, and one must know these technologies well.
Ownership, Support, and Key Customers
HBase is an open-source database developed and maintained by the Apache Software Foundation, and commercial technical support is provided by several Hadoop vendors.
Some of HBase’s prominent customers include Adobe, Netflix, Pinterest, Salesforce, Spotify, and Yahoo.
3. Hive
Hive: It is a platform used to develop SQL type scripts to do MapReduce operations. Apache Hive is a data warehouse framework for querying and analysis of data stored in HDFS. It is developed on top of Hadoop. Hive is an open-source software to analyze large data sets on Hadoop. It provides SQL-like declarative language, called HiveQL, to express queries. Using Hive-QL, users associated with SQL can perform data analysis very easily.
Initially Hive was developed by Facebook, later the Apache Software Foundation took it up and developed it further as an open source under the name Apache Hive. It is used by different companies. For example, Amazon uses it in Amazon Elastic MapReduce.
Hive is not
- A relational database
- A design for OnLine Transaction Processing (OLTP)
- A language for real-time queries and row-level updates
Features of Hive
- It stores schema in a database and processed data into HDFS.
- It is designed for OLAP.
- It provides SQL type language for querying called HiveQL or HQL.
- It is familiar, fast, scalable, and extensible.
Hive Vs Map Reduce
Prior to choosing one of these two options, we must look at some of their features.
While choosing between Hive and Map reduce following factors are taken in consideration;
- Type of Data
- Amount of Data
- Complexity of Code
4. MongoDB
Overview and Features
MongoDB is the most popular document store on the market and is also one of the leading Database Management Systems. It was created in 2007 by the team behind DoubleClick (currently owned by Google) to address the scalability and agility issues in serving Internet ads by DoubleClick.
MongoDB offers both a community and an enterprise version of the software. The enterprise version offers additional enterprise features like LDAP, Kerberos, auditing, and on-disk encryption.
MongoDB Advantages and Use Cases
MongoDB is a schema-less database and stores data as JSON-like documents (binary JSON). This provides flexibility and agility in the type of records that can be stored, and even the fields can vary from one document to the other. Also, the embedded documents provide support for faster queries through indexes and vastly reduce the I/O overload generally associated with database systems. Along with this is support for schema on write and dynamic schema for easy evolving data structures.
MongoDB also provides several enterprise features, like high availability and horizontal scalability. High availability is achieved through replica sets which boast features like data redundancy and automatic failover. This ensures that your application keeps serving, even if a node in the cluster goes down.
MongoDB also provides support for several storage engines, ensuring that you can fine-tune your database based on the workload it is serving. Some of the most common use cases of MongoDB include a real-time view of your data, mobile applications, IoT applications, and content management systems. Finally, it includes a nested object structure, indexable array attributes, and incremental operations
MongoDB Disadvantages
Unless you opt for one of the DBaaS flavors, management operations like patching are manual and time-consuming processes. Although it has improved in the newer versions, MapReduce implementations still remain a slow process, and MongoDB also suffers from memory hog issues as the databases start scaling.
Ownership, Support, and Key Customers
MongoDB is owned by MongoDB, Inc., with its headquarters in New York. The community version is free to use and is supported by the MongoDB community of developers and users on its community forum. On the other hand, the enterprise version is supported by MongoDB, Inc. engineers 24/7.
As one of the most popular databases on the market, MongoDB counts names like eBay, Google, Cisco, SAP, and Facebook among its clients.
5. Neo4j
Neo4j is the world's leading open source Graph Database which is developed using Java technology. It is highly scalable and schema free (NoSQL).
Graph database is a database used to model the data in the form of graph. In here, the nodes of a graph depict the entities while the relationships depict the association of these nodes.
Popular Graph Databases
Neo4j is a popular Graph Database. Other Graph Databases are Oracle NoSQL Database, OrientDB, HypherGraphDB, GraphBase, InfiniteGraph, and AllegroGraph.
Features of Neo4j
Following are the notable features of Neo4j −
Data model (flexible schema) − Neo4j follows a data model named native property graph model. Here, the graph contains nodes (entities) and these nodes are connected with each other (depicted by relationships). Nodes and relationships store data in key-value pairs known as properties.
In Neo4j, there is no need to follow a fixed schema. You can add or remove properties as per requirement. It also provides schema constraints.
ACID properties − Neo4j supports full ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability) rules.
Scalability and reliability − You can scale the database by increasing the number of reads/writes, and the volume without effecting the query processing speed and data integrity. Neo4j also provides support for replication for data safety and reliability.
Cypher Query Language − Neo4j provides a powerful declarative query language known as Cypher. It uses ASCII-art for depicting graphs. Cypher is easy to learn and can be used to create and retrieve relations between data without using the complex queries like Joins.
Built-in web application − Neo4j provides a built-in Neo4j Browser web application. Using this, you can create and query your graph data.
Drivers − Neo4j can work with −
REST API to work with programming languages such as Java, Spring, Scala etc.
Java Script to work with UI MVC frameworks such as Node JS.
It supports two kinds of Java API: Cypher API and Native Java API to develop Java applications. In addition to these, you can also work with other databases such as MongoDB, Cassandra, etc.
Indexing − Neo4j supports Indexes by using Apache Lucence.
Advantages of Neo4j
Following are the advantages of Neo4j.
Flexible data model − Neo4j provides a flexible simple and yet powerful data model, which can be easily changed according to the applications and industries.
Real-time insights − Neo4j provides results based on real-time data.
High availability − Neo4j is highly available for large enterprise real-time applications with transactional guarantees.
Connected and semi structures data − Using Neo4j, you can easily represent connected and semi-structured data.
Easy retrieval − Using Neo4j, you can not only represent but also easily retrieve (traverse/navigate) connected data faster when compared to other databases.
Cypher query language − Neo4j provides a declarative query language to represent the graph visually, using an ascii-art syntax. The commands of this language are in human readable format and very easy to learn.
No joins − Using Neo4j, it does NOT require complex joins to retrieve connected/related data as it is very easy to retrieve its adjacent node or relationship details without joins or indexes.
REF
https://searchdatamanagement.techtarget.com/definition/Hadoop-Distributed-File-System-HDFS
https://www.guru99.com/hive-tutorials.html
https://www.ibm.com/analytics/hadoop/hbase